- India
- International
Joko Widodo sworn in as Indonesia’s seventh president
Widodo is the first Indonesian president not to come from the ranks of the country's established political, business and military elite.
 Indonesian President Joko Widodo, center, shouts “freedom” while raising his fist as he delivers his speech during his inauguration ceremony as the country’s seventh president at the parliament building in Jakarta, Indonesia, Monday, Oct. 20, 2014. (Source: AP)
Indonesian President Joko Widodo, center, shouts “freedom” while raising his fist as he delivers his speech during his inauguration ceremony as the country’s seventh president at the parliament building in Jakarta, Indonesia, Monday, Oct. 20, 2014. (Source: AP)
Joko Widodo was inaugurated as Indonesia’s new president on Monday, facing the challenges of rebooting a slowing economy and working with a potentially hostile opposition that has already landed some early blows against his administration.
Widodo, the first Indonesian president not to come from the ranks of the country’s established political, business and military elite, took the oath of office in a ceremony at parliament in the capital, Jakarta, attended by regional leaders and U.S. Secretary of State John Kerry.
 Indonesian President Joko Widodo, left, and his predecessor Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono pray during Widodo’s inauguration ceremony as the country’s seventh president at the Parliament building in Jakarta, Indonesia, Monday, Oct. 20, 2014. Widodo was inaugurated as Indonesia’s new president on Monday, facing the challenges of rebooting a slowing economy and working with a potentially hostile opposition that has already landed some early blows against his administration. (Source: AP)
Indonesian President Joko Widodo, left, and his predecessor Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono pray during Widodo’s inauguration ceremony as the country’s seventh president at the Parliament building in Jakarta, Indonesia, Monday, Oct. 20, 2014. Widodo was inaugurated as Indonesia’s new president on Monday, facing the challenges of rebooting a slowing economy and working with a potentially hostile opposition that has already landed some early blows against his administration. (Source: AP)
“To the fishermen, the workers, the farmers, the merchants, the meatball soup sellers, the hawkers, the drivers, the academics, the laborers, the soldiers, the police, the entrepreneurs and the professionals, I say let us all work hard, together, shoulder to shoulder, because this is a historic moment,” Widodo, popularly known as “Jokowi,” said in his inauguration address.
He ended his speech with a shout of “Merdeka!” or “Freedom,” the independence-era rallying cry associated with the country’s founding president, Sukarno.
 Indonesian President Joko Widodo, center, reads his oath during his inauguration ceremony as the country’s seventh president at the parliament building in Jakarta, Indonesia, Monday, Oct. 20, 2014. (Source: AP)
Indonesian President Joko Widodo, center, reads his oath during his inauguration ceremony as the country’s seventh president at the parliament building in Jakarta, Indonesia, Monday, Oct. 20, 2014. (Source: AP)
A former furniture salesman, the 53-year-old Widodo rose from humble beginnings to become Jakarta’s governor before winning July’s presidential election with 53 percent of the vote. Polls showed most of his support came from lower-income, non-urban Indonesians attracted by his simple demeanor and record of honest, hard work.

Indonesia is the biggest economy in Southeast Asia, and about 90 percent of its 250 million people are Muslims, more than any other nation. After years of dictatorship, the country was convulsed by political, ethnic and religious unrest in the late 1990s and early 2000s. Since then, it has consolidated its democratic transition. While most of the country remains poor, it is home to a rapidly expanding middle class.
 Prabowo Subianto a political rival to Indonesia’s seventh President Joko Widodo’s gestures as he arrives ahead of Widodo’s inauguration at Parliament in Jakarta, Indonesia, Monday, Oct. 20, 2014. (Source: AP)
Prabowo Subianto a political rival to Indonesia’s seventh President Joko Widodo’s gestures as he arrives ahead of Widodo’s inauguration at Parliament in Jakarta, Indonesia, Monday, Oct. 20, 2014. (Source: AP)
Outgoing President Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono’s two terms in office saw democratic consolidation and a focused fight against Islamist militancy. But economic growth on the back of a commodities boom has slowed, and a recovery is being hampered by weak infrastructure, rampant corruption and red tape.
Economic growth is currently around 5 percent, barely allowing enough jobs to be created. Widodo is targeting 7 percent growth in the coming years. To get close to that, he will need bold reforms to attract foreign investment and favorable external conditions. A looming problem is expected hikes next year in what are record-low U.S. interest rates, which could suck funds from the country, pressurizing the rupiah and spooking the markets.
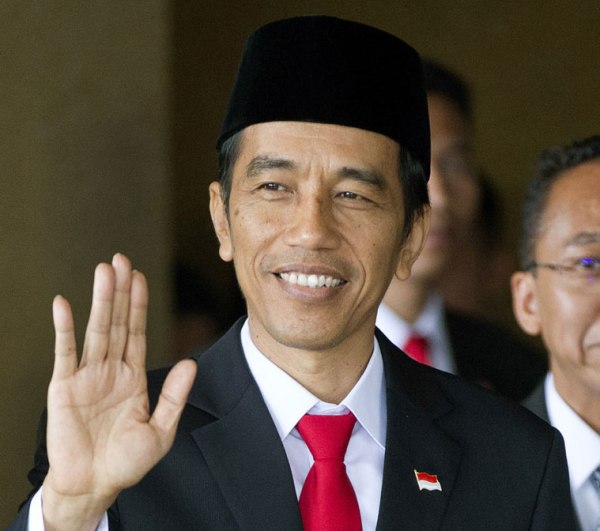 Joko Widodo waves ahead of his swearing in as Indonesia’s seventh president at Parliament in Jakarta, Indonesia, Monday, Oct. 20, 2014. (Source: AP)
Joko Widodo waves ahead of his swearing in as Indonesia’s seventh president at Parliament in Jakarta, Indonesia, Monday, Oct. 20, 2014. (Source: AP)
Economists say Widodo must soon make a decision on how much to cut subsidies on fuel that unless trimmed will cost the government a budget-busting $30 billion-plus this year. The move will likely stoke protests from political opponents and could trigger street demonstrations.
He can also expect resistance from opposition parties still smarting from the election defeat of their candidate, Prabowo Subianto, a wealthy general with close ties to Indonesia’s former dictator Suharto. The coalition against Widodo already has captured most of the important positions in parliament and last month voted to end direct regional elections, a key plank of the country’s democratic transition since Suharto was ousted in 1998.
Subianto attended Monday’s inauguration ceremony and met with Widodo last week to offer qualified support for his administration. Much uncertainty remains over how effective Widodo will be in negotiating with the opposition, and how much of a disruptive role it will play. Subianto’s initial refusal to accept the election results and the comments of some of his supporters led to speculation among analysts that he would seek to topple Widodo midterm.
In his inauguration speech, Widodo pledged to maintain the country’s “free and active” foreign policy, a stance that has seen it slowly taking up more of a leadership role in Southeast Asia. Working to stop the flow of foreign fighters to Iraq and Syria, managing relations with China and keeping often testy ties with Australia on an even keel will be key tasks.
“I’m very encouraged by everything that President Jokowi has said up until now. He’s obviously a charismatic and inspirational figure,” said Australian Prime Minister Tony Abbott, who flew to Jakarta for the ceremony. “I think there’s a wave of confidence and renewal sweeping Indonesia right now.”
Apr 19: Latest News
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05