In the rapidly evolving world of higher education and training, colleges and universities have a unique opportunity to leverage technology for the benefit of their student employees.

Working a part-time job while attending a college or university is usually a solution that can help students pay for personal expenses, supplement financial aid, and gain valuable work experience. Part-time work is also very common, especially with the rising price of tuition and the burden of student loan debt. Statistics for 2022 show that 43 percent of full-time students and 81 percent of part-time students worked while enrolled at a higher education institution.Footnote1
Many of these students work at their institution. Colleges and universities rely heavily on this large base of student employees, who play a crucial role in advancing the success of the institution's initiatives. However, student employees often encounter scheduling challenges, primarily stemming from the unpredictability of their availability due to academic commitments. The utilization of technology, particularly mobile-first solutions, not only facilitates seamless access but also enhances accountability among student workers.Footnote2
In today's fast-paced world, technology has become an indispensable tool for both educators and trainers. According to the results from an EDUCAUSE QuickPoll, hybrid/online learning may be here to stay.Footnote3 Instructional designers, learning experience designers, and training and development experts have a unique opportunity to harness the power of technology to create more effective and engaging training programs for student employees in higher education. This in turn gives students an advantage for balancing work and study.
What are the benefits of using technology to train student employees, and what are the most effective strategies to enhance the learning experience of student employees? At the University of Tampa's Information Technology and Security (ITS) department, our goal is to make technology accessible, reliable, and user-friendly for all members of the community, including student employees. The ITS Media Services thus launched an online training course during the fall semester of 2023 (16 students) and again in spring 2024 (5 students). The course uses an interactive learning experience for student employees to effectively apply their skills as audio visual (AV) technicians at Media Services events. The goal when developing the online course was to intentionally leverage the latest advancements in educational technology and provide a tangible impact on student employees' training.Footnote4
Enhanced Engagement and Interactive Learning
Incorporating technology when providing instructions allows trainers to create interactive content—such as simulations, discussion boards, and gamified activities—and can increase engagement more than traditional training methods. Since students are likely to utilize technology for educational purposes, it makes sense to incorporate it when training them to be effective employees. The key is to prioritize user experience and design to make the training process engaging, intuitive, and enjoyable for learners. Adapting learning technologies can also help instructional designers tailor training programs to the needs of individual students, ensuring that no one falls behind or gets bored. Another factor to consider is offering content in various mediums—such as videos, interactive quizzes, and written materials—that cater to different learning styles and preferences of learners. This user-friendly approach to design significantly enhances the overall learning journey for student employees.
Workplace Readiness and Employee Retention
As a previous student employee at ITS Media Services, I saw firsthand how the institution focused heavily on developing my skill set and upholding workplace readiness. Technological innovations led me to return to the institution to work as a full-time employee. These skills translated to my advancement into a managerial role as a media services specialist, where I supervised students' performance and implemented effective training strategies.
After my return, I quickly realized that there was a huge learning gap needing to be filled. I decided to utilize my acquired knowledge as an instructional designer to develop new ways to provide the next generation of student employees with better learning experiences and retention of knowledge through the online training. By incorporating technology into their training, I helped student employees gain valuable digital literacy skills that assisted them in advancing in their roles. These skills are also increasingly essential in today's workforce and are directly transferable to future positions.
Instructional designers can implement technology-driven training to prepare student employees to adapt to evolving work environments, enabling them to stay relevant in their careers and prepared for the workforce after they graduate from their designated program. Developing digital literacy helps meet training goals such as fostering critical thinking, customer service, and problem-solving skills to meet the demands of the workplace. This training can also prepare student employees to stay at or return to their institution and become major contributors to and investors in the advancement of future generations of students.
Inclusivity and Belonging
Online platforms and mobile apps enable student employees to navigate training materials at their convenience, allowing them to balance work and study commitments more easily. If created in a way that is accessible and if designed using models such as the Universal Design for Learning (UDL) framework, these platforms and apps can also help meet students' accommodation needs.Footnote5 UDL focuses on developing inclusive learning environments. Platforms such as Canvas, Blackboard, and Articulate give students with disabilities an equitable opportunity to acquire skills through features such as alternative formats, electronic braille, and text-to-speech when training is delivered online. The online learning environment offers students a sense of belonging and inclusivity, since features are offered for all within the platforms. Ideally, UDL not only allows students with disabilities to access courses without adaptation but also allows the learning content to be available in a variety of formats for everyone to access.
After I changed roles at the University of Tampa and became an academic accessibility technologist in the ITS department, I developed a mission to further accessibility efforts at the institution. I work with various departments to provide all students with an equal opportunity to experience learning through acquiring skills and knowledge. I meet with faculty to ensure that their course content is accessible for all students by facilitating workshops and training and having one-on-one coaching sessions to guide them on how to make their courses more accessible (e.g., using the ALLY tool in the Canvas LMS). To consistently implement UDL fundamentals, I advise faculty on how to provide captions in videos, offer alternative text and formats for content, and remediate Microsoft Word and PDF documents for accessibility. I also collaborate with the Student Accessibility Services departments to be sure that we are meeting the needs of students who have specific accommodation requests.
Convenience, Time, and Cost-Efficiency
Online resources eliminate the need for physical training materials, reducing the costs associated with printing and shipping. Technology allows for easy scaling of training programs, making online training cost-effective for organizations with growing numbers of student employees. It also reduces the time required for in-person scheduling and meetings for training. This allows trainers the ability to track student employees' performance in and completion of the training and offers valuable feedback and recognition in a convenient and timely manner, which in turn increases the motivation that is essential in all learning environments.Footnote6
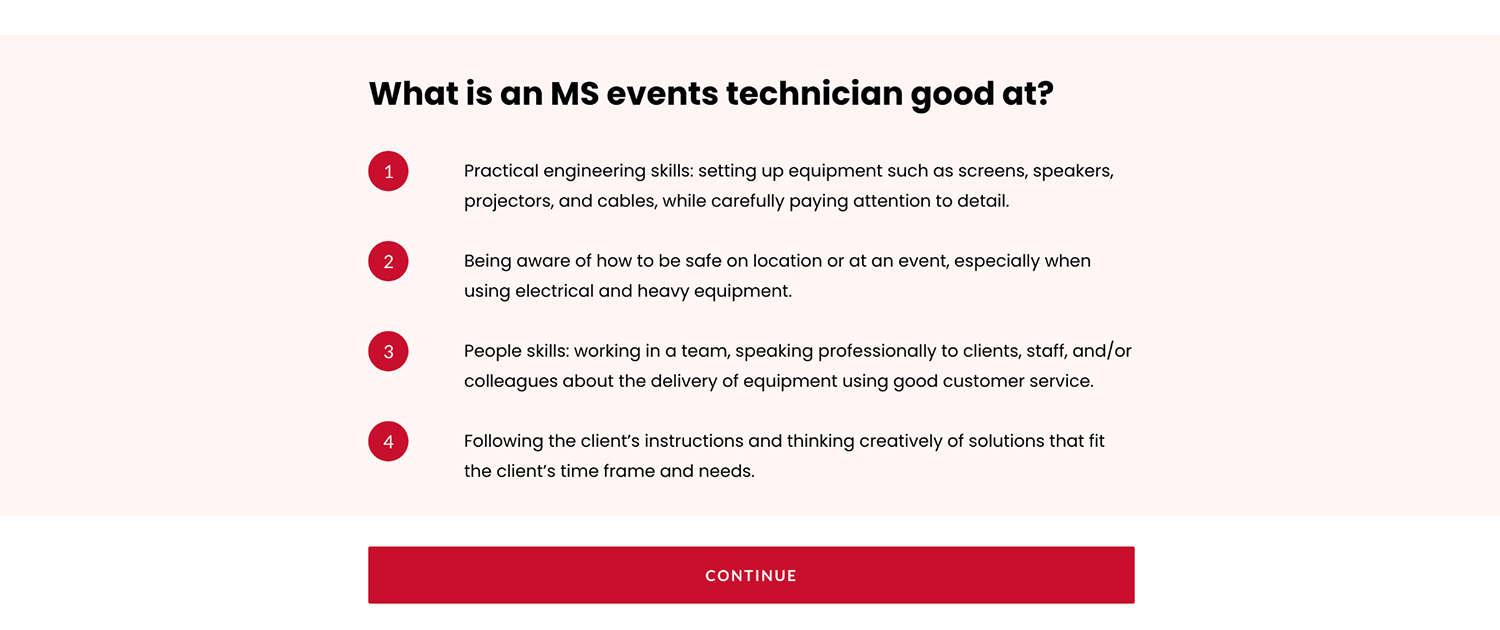
Some of the instructional technologies available today provide content in bite-sized, easily consumable modules. This practice allows learners to access information quickly and efficiently. This method of learning has been shown to be effective for knowledge retention and for students' overall success in acquiring current and evolving information.Footnote7 This method is applied in the Media Services Events course under the Media Services Equipment Module, which gives student employees an interactive experience in which they can view the image of the equipment with a brief description of the equipment name and what it is used for.
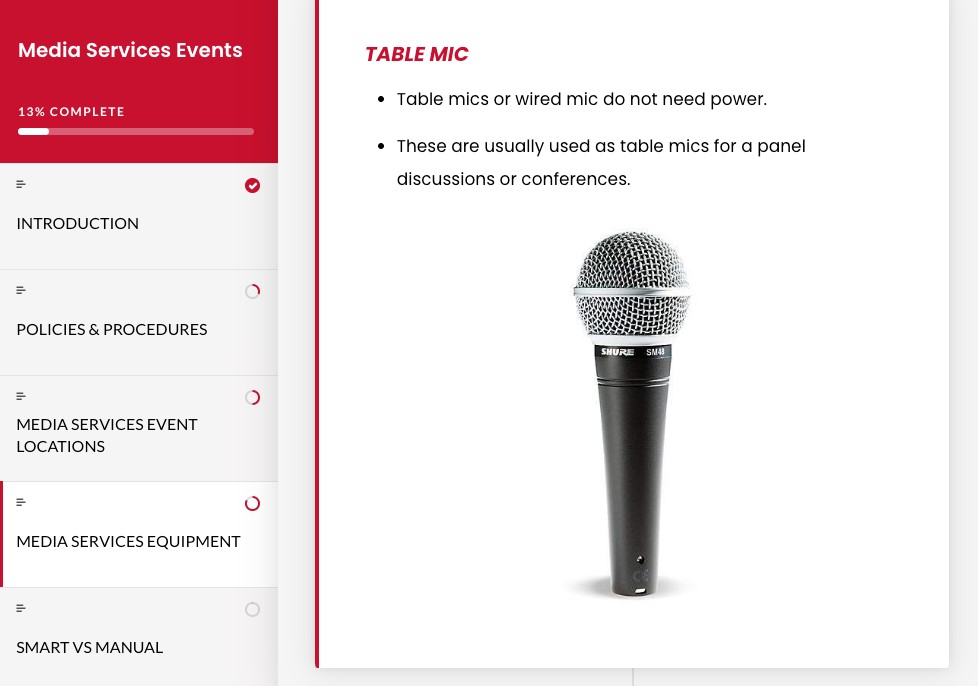
Finally, technology transcends geographical boundaries, facilitating the training of student employees in different locations or time zones. This also offers the opportunity to deliver training materials globally to prepare students who are studying abroad or are away for vacation.
Assessments, Feedback, and Data-Driven Insights
Technology provides valuable data on students' performance, allowing trainers to adapt and improve materials in real time. Analyzing data can help us identify areas where student employees may be struggling, enabling us to provide additional support.
Our online training course includes a final exam, with a minimum 80% score required to pass the training. Students have three attempts to achieve the 80% score. If a score is less than 80%, students can meet with a trainer to review problem areas to ensure that they are acquiring the information they need to be successful at their jobs. After the course was completed by 16 student employees in the Fall 2023 semester, we collected results from the final assessment. The good news was that 62.5% of the students achieved a 100% score, 25% of the students achieved a 90–99% score, and 12.5% of students received an 80–89% after completing the assessment. These scores not only measured the level of understanding and test knowledge but also provided more insight into how effective the online course was for the students.
After the students completed the online training course in the fall of 2023, we sent out a comprehensive survey to get feedback on their overall experience. Students were required to answer questions using a Likert scale and also provide feedback anonymously. Results showed that after having completed the online training course, 66% percent reported they were extremely satisfied with completing their expected tasks (i.e., successfully setting up AV equipment for their assigned events, providing great customer service, and following the correct policies and procedures), while 33% were somewhat satisfied. In addition, 100% of the students reported that the online training course was helpful and that they were more familiar with the policies and procedures of their role after completion of the course.
Conclusion
In the rapidly evolving world of higher education and training, instructional designers have a unique opportunity to harness the power of technology for the benefit of student employees. The use of technology enhances engagement, workplace readiness, accessibility, and cost-efficiency while providing valuable data-driven insights. By embracing technology in student employee training programs, colleges and universities not only prepare student employees for the demands of the modern workforce but also future-proof their skills, ensuring they remain competitive in an ever-changing job market.
Notes
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, "Labor Force Participation Rates of College Students Differ by Enrollment Status and Type of College," The Economics Daily, May 24, 2023. Jump back to footnote 1 in the text.
- Sam Campbell, "How to Handle the Challenges of Scheduling Student Employees," When I Work (blog), October 31, 2023. Jump back to footnote 2 in the text.
- Mark McCormack, "EDUCAUSE QuickPoll Results: Assessment and Learning Design," EDUCAUSE Review, April 2, 2021. Jump back to footnote 3 in the text.
- The course was developed on the Articulate Rise 360 platform and then, via SCORM, integrated into the Canvas Instructure learning management system. This made the course easier for students to access. Although both platforms are very intuitive for learners and developers and are easy to navigate, Canvas is the platform utilized by our institution. Jump back to footnote 4 in the text.
- Cindy Ann Dell, Thomas F. Dell, and Terry L. Blackwell, "Applying Universal Design for Learning in Online Courses: Pedagogical and Practical Considerations," Journal of Educators Online 12, no. 2 (2015). Jump back to footnote 5 in the text.
- Katy A. Ventura, "Motivation in Student Employees in the Workforce and the Effect It Has on Their Work," Reach, no. 4 (Fall 2020). Jump back to footnote 6 in the text.
- Rene Corbeil and Maria Elena Corbeil, "Microlearning: The 'OG' or Hot New Trend?" EDUCAUSE Review, August 2, 2023; Rizwan Khan, "Engaging Minds: The Interactive Learning Experience of eLearning," eLearning Industry, June 24, 2023. Jump back to footnote 7 in the text.
Irene Sidede is Academic Accessibility Technologist, Information Technology and Security, at the University of Tampa.
© 2024 Irene Sidede. The content of this work is licensed under a Creative Commons BY-NC-ND 4.0 International License.
