Urban land use
The land in urban areas is used for many different purposes:
- Leisure and recreation - may include open land, e.g. parks or built facilities such as sports centres
- Residential - the building of houses and flats
- Transport - road and rail networks, stations and airports
- Business and commerce - the building of offices, shops and banks
- Industry - factories, warehouses and small production centres
The CBD (Central business district)

The central business district (CBD)The CBD is the central downtown area which contains the main commercial streets and public buildings. It is the core of the city’s business and civic life and is the place where business and retail meet. in the city centre is where most business and commerce is located.
A CBD can be identified by some of the following:
- high/multi-storey buildings
- expensive land values
- department stores or specialist shops, like jewellers
- shopping malls and pedestrian precincts
- cultural/historical buildings, museums and castles
- offices, finance, banks, administration, town hall (business sector)
- bus and railway stations (transport centres)
- multi-storey car parks
The CBD is located in the centre because it is:
- a central location for road/railways to converge
- the most accessible location for workers
- accessible to most people for shops and businesses
The inner city
The inner city is typically found next to the CBD and has mainly terraced houses in a grid like pattern. These were originally built to house factory workers who worked in the inner city factories. These inner city areas often had strong communities but, with many factories in inner cities closing, there was more unemployment and a lack of investment. Many inner city areas declined in the late 20th century. Some have experienced regeneration in recent years.
Unemployment and other socioeconomic problems have led to periods of unrest in many inner city areas. Many inner city areas declined in the late 20th century and have undergone a period of regeneration in recent years..In some cases, run down terraced housing is bought by investors and improved to appeal to young professionals who like to live near to the CBD for work and entertainment. This is called gentrificationGentrification is the process when an area is redeveloped and upgraded, attracting richer people and often displacing poorer tenants so that richer people will move into the more expensive, new, modern, accommodation. . It may help to improve the appearance of some inner city areas, but it may make these houses too expensive for local people, which damages the communities who live there.

The suburbs is a mostly residential area located on the outskirts of a town or city.
Suburban houses are usually larger than inner city terraces and most have a garden. Typically, they are detached or semi-detached and the roads around them are arranged in cul-de-sacs and wide avenues.
Land prices are generally cheaper than in the CBD and inner city, although the desirability of housing can make some areas expensive.
Facilities such as schools, places of worship and parks are often present, and many are served by a local supermarket.
The suburbs are often home to commuters who need access to the CBD along main roads and railways, and they are also within easy reach of the countryside.

The rural-urban fringe is the land on the edge of an urban area where the urban area ends and the rural area beings. It is common for this area to have a mixture of land uses such as some housing, golf courses, allotments, business parks and airports.
The mixture of land use often causes conflict as different groups have different needs and interests. For example, building Terminal 5 at Heathrow on the outskirts of London was a source of controversy. The need for another runway continues to cause conflicts of interest.
The function of settlements
A settlement is a place where people live. Settlements can be as small as a single house in a remote area or as a large as a mega city (a city with over 10 million residents).
A settlement may be permanent or temporary. An example of a temporary settlement is a refugee camp. However, a temporary settlement may become permanent over time. This has happened to many refugee campA refugee camp is a temporary settlement built to receive refugees and people in refugee-like situations. Refugee camps usually accommodate displaced persons who have fled their home country, but there are also camps for internally displaced persons. that have been built in conflict zones.
The function of a settlement helps to identify the economic and social development of a place and can show its main activity. Most large settlements have more than one function though in the past one function was maybe the most important in defining the success and growth in importance of the settlement.

The main functions of a settlement are:
- Market town – where farmers will buy and sell their goods and materials
- Mining town – where minerals and fuel might be extracted
- Industrial town – where raw materials will be processed into manufactured products
- Port – a place where goods can be imported and exported
- Route centre – a place where several important roads/ transport links will meet
- Service centre – a place that will provide for the main needs and services for people living in a particular area
- Cultural/ Religious centre – a place that will welcome people from different places for learning or religious observance
- Administrative centre – where government offices and departments will be located
- Residential town – a place where people will live but will travel to work somewhere else
- Tourist resort – where people visit to relax and enjoy themselves
Using aerial photographs
Aerial photos can be used to help identify urban features. For example, geographers might be able to look at the patterns seen in a city and identify whichland use zoneThis is the function of the land use i.e what the land is predominately used for in a particular area that shows.
The different uses and functions of the land use could also be identified at both the urban and rural levels.

Urban areas such as that shown of Belfast above can often be very easy to recognise.
The CBD tends to have a high density of buildings as this helps to maximise on the expensive ground rents in the area. Also, most CBDs usually display a more planned ‘grid’ like pattern.
The Inner City can be easily recognised as there are large areas of grey/brown field sites where factories are located. In older cities, long rows of terraced houses will be found close to the industrial areas so that factory workers could live in close proximity to their place of work.
The Suburbs can be more difficult to find as these residential areas usually consist of larger houses that might have gardens and/or garages. This is not always immediately obvious on aerial photos and satellite images. However, a tell-tale sign of more modern buildings is that roads are not as straight and often involve loops and cul-de-sacs.
The rural-urban fringe can be found on the very edge of the city where the city and rural areas meet. Houses here tend to be much bigger and often are isolated from their neighbours.
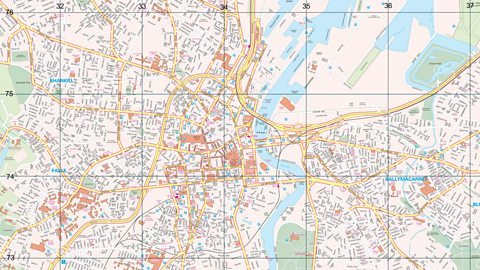
Using OS maps to identify settlement features
Identifying the land use zones of settlements
You should be able to use aerial photos and OS maps to identify the four differentland use zones – the CBD, Inner City, Suburbs and the rural-urban fringeThe city was continuing to expand into the countryside and the boundary between urban and rural areas was rapidly becoming blurred.
What are some of the features you would expect to see in each zone?
| CBD | Inner City | Suburbs | Rural-urban fringe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tightly packed roads, town hall, city centre, bus and railway stations, car parks, shops and government offices | Straight roads with terraced houses, factories and industrial areas, possibly evidence of some re-development | Residential areas, with bigger houses, garages and more space. Roads will not be as straight and possible cul-de-sacs | Much further from the CBD, often beyond the edge of the city, on the other side of green space |
Watch: Urban land use video
How urban land is used in MEDCs
Activity: Take the test
More on Changing urban areas
Find out more by working through a topic
- count3 of 4

- count4 of 4
