You may consider business protection as arming the security system at your offices or stores at the end of the day or ensuring the safety of warehoused inventory.
Your company's computer network, however, contains equally valuable customer information, financial data, and other proprietary records. And just as every door and window is a potential point of entry by bad actors, so is every device, aka "endpoint," connected to your network.
A recent study showed 28% of respondents reported endpoint breaches via multiple threat vectors:
- Social engineering/phishing (58%)
- Web drive-by (52%)
- Credential theft/compromise (49%)
Protecting your network and data is critical for uninterrupted business operations. We'll go over the basics of endpoint security and its different functions, so you can see how it will benefit your small business.
Overview: What is endpoint security?
Endpoint security solutions are cybersecurity software that secures devices such as servers, desktop computers, laptops, tablets, and smartphones connected to a larger network.
These applications extend network and device defenses beyond traditional antivirus software and include device management, data leak protection (DLP), and threat detection and investigation.
Endpoint security applications use an endpoint protection platform (EPP), which is installed on endpoints, to protect against malware and other intrusions. An EPP may be combined with an endpoint detection and response (EDR) platform that focuses on monitoring, threat detection, and responses.
Endpoint security can use the client-server model for the internal protection of a company's enterprise network or be web-based software-as-a-service (SaaS).
The latter option, for example, is used for electronic payment processing to secure consumer financial data as it's transferred between multiple companies. Both models continually monitor, analyze, and resolve threats to protect network assets and ensure regulatory security compliance.
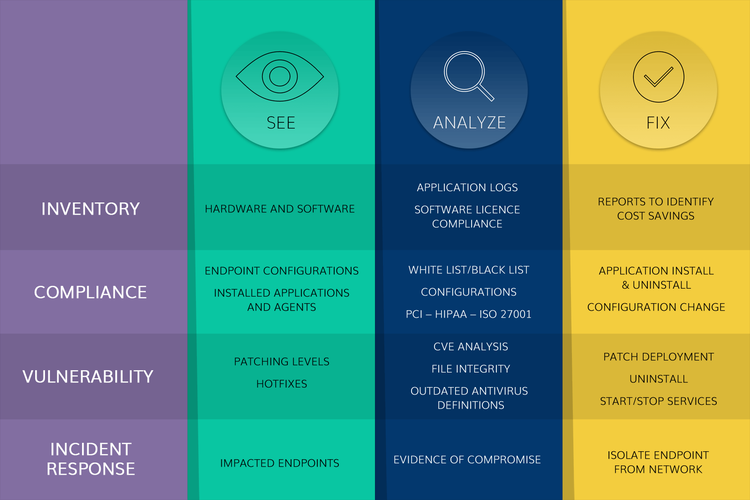
Endpoint security uses a multifaceted approach to protect an enterprise network. Image source: Author
A security operations center (SOC) oversees endpoint security as part of its cybersecurity plan for one or more enterprise networks. Endpoint security contributes directly to the SOC's two primary responsibilities: proactive policy management and reactive monitoring and responses.

Endpoint security is one level of protection in an enterprise network. Image source: Author
While consumers can buy off-the-shelf endpoint protection applications, these are primarily reactive and don't have the customization options or wide-ranging features enterprise solutions offer.
How does endpoint security work?
Endpoint security consists of multiple activities -- encrypting data, blocking social engineering phishing attempts, and thwarting ransomware attacks -- to protect devices connected to an enterprise network.
We'll go over the most common endpoint data protection functions below to demonstrate how they could benefit your small business's network.
Password protection
Endpoint control starts with robust password policies to prevent unauthorized access to endpoint devices. This requires regularly scheduled password updates and employing password protocols to prevent the use of too-common passwords such as "12345" and "password."
A dedicated password manager application that employs two-factor authentication is also essential endpoint security technology.
Endpoint encryption
Each device connected to your network, from a USB memory stick to a server, potentially contains sensitive data such as customer names and addresses, financial information, and other confidential business records.
Endpoint encryption, which securely encodes all data transmitted from a device via the web, greatly reduces the odds of bad actors accessing this information or installing malware.
Secure email gateway (SEG)
Prevent email-based threats from reaching an onsite email server or a cloud email service such as Gmail with a secure email gateway (SEG).
A SEG also offers protection from social engineering attacks, including phishing, pretexting, and baiting, and can scan messages for suspicious content. Many SEGs have archiving features to store emails for regulatory and legal compliance.
URL filtering
A URL filter uses a constantly updated web address database to prevent employees from visiting malicious websites. Every website address in the database is categorized and allowed or blocked based on its URL category.
URL filtering database information can come from an analysis of your company's website traffic or external sources such as cybersecurity provider McAfee.

If you see this warning, run for your life! Image source: Author
Beyond network and data protection, URL filtering can also prevent employees from spending big chunks of their day surfing social media sites, shopping at online stores, or researching upcoming trips.
Antivirus protection
While many endpoint security activities such as URL filtering are systemwide, endpoint antivirus applications are installed on individual devices. Regularly scheduled or manual scans detect malware such as spyware, trojan horses, worms, and ransomware.
Antivirus software updates automatically, so the endpoint is protected from the latest threats.
What is the importance of endpoint security?
Endpoint security is critical to protect your network and its information from data breaches and avoid financial losses due to costly remediation efforts and regulatory penalties. The nature of these threats is evolving as enterprise networks expand and add more endpoints.
Emerging endpoint security threats include:
- Remote workforces: More people than ever are working remotely due to the COVID-19 pandemic, and companies such as Google and Facebook have announced plans to keep many employees offsite for at least a year. One result is the proliferation of personal devices on company networks, a perpetual bring your own device (BYOD) day with the accompanying security threats.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Beyond endpoints such as computers, mobile devices, and servers, the IoT includes other interrelated computing devices -- sensors, closed-circuit television (CCTV) cameras, environmental controls -- that transfer data over a network with no human interaction. The result is more access points for potential data breaches.
- Ransomware attacks: Cyber criminals use ransomware to demand payment from a victim under the threat of publishing sensitive data or permanently blocking access to it. These attacks have grown in frequency since 2012, and U.S. companies and government agencies lost an estimated $7.5 billion from them in 2019.
Every data breach also undermines consumer confidence in your company, which is compounded if you're caught concealing it.
Ride-sharing company Uber's former chief security officer was criminally charged in August 2020 for paying $100,000 to hackers to cover up a 2016 hack that exposed the personal information of about 57 million customers and drivers.
Protect your network and data with endpoint security
Endpoint security consists of more than forwarding a link to the latest "How to Make a Strong Password" article to your employees. (Although we've got you covered on that front, too!)
It's not a bad place to start. Instead of an ad hoc collection of protocols and applications, consider using the best integrated endpoint security software. Unified virus and threat protection will maximize your results and save time and money.
Our Small Business Expert
We're firm believers in the Golden Rule, which is why editorial opinions are ours alone and have not been previously reviewed, approved, or endorsed by included advertisers. The Ascent, a Motley Fool service, does not cover all offers on the market. The Ascent has a dedicated team of editors and analysts focused on personal finance, and they follow the same set of publishing standards and editorial integrity while maintaining professional separation from the analysts and editors on other Motley Fool brands.