Caterpillar Inc. (NYSE:CAT) Delivered A Better ROE Than Its Industry

Want to participate in a short research study? Help shape the future of investing tools and you could win a $250 gift card!
While some investors are already well versed in financial metrics (hat tip), this article is for those who would like to learn about Return On Equity (ROE) and why it is important. We’ll use ROE to examine Caterpillar Inc. (NYSE:CAT), by way of a worked example.
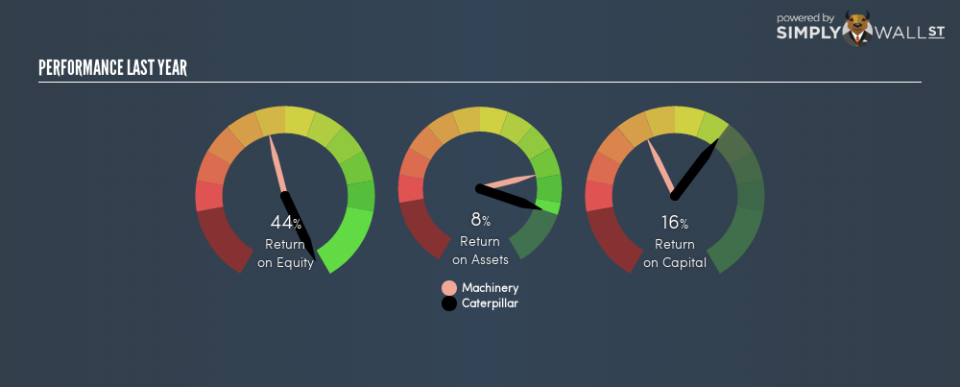
Caterpillar has a ROE of 44%, based on the last twelve months. One way to conceptualize this, is that for each $1 of shareholders’ equity it has, the company made $0.44 in profit.
Check out our latest analysis for Caterpillar
How Do You Calculate ROE?
The formula for ROE is:
Return on Equity = Net Profit ÷ Shareholders’ Equity
Or for Caterpillar:
44% = 6147 ÷ US$14b (Based on the trailing twelve months to December 2018.)
It’s easy to understand the ‘net profit’ part of that equation, but ‘shareholders’ equity’ requires further explanation. It is the capital paid in by shareholders, plus any retained earnings. Shareholders’ equity can be calculated by subtracting the total liabilities of the company from the total assets of the company.
What Does ROE Mean?
ROE looks at the amount a company earns relative to the money it has kept within the business. The ‘return’ is the yearly profit. The higher the ROE, the more profit the company is making. So, all else equal, investors should like a high ROE. That means ROE can be used to compare two businesses.
Does Caterpillar Have A Good Return On Equity?
Arguably the easiest way to assess company’s ROE is to compare it with the average in its industry. Importantly, this is far from a perfect measure, because companies differ significantly within the same industry classification. As you can see in the graphic below, Caterpillar has a higher ROE than the average (14%) in the Machinery industry.
That is a good sign. I usually take a closer look when a company has a better ROE than industry peers. For example you might check if insiders are buying shares.
The Importance Of Debt To Return On Equity
Most companies need money — from somewhere — to grow their profits. That cash can come from retained earnings, issuing new shares (equity), or debt. In the first and second cases, the ROE will reflect this use of cash for investment in the business. In the latter case, the debt required for growth will boost returns, but will not impact the shareholders’ equity. That will make the ROE look better than if no debt was used.
Combining Caterpillar’s Debt And Its 44% Return On Equity
Caterpillar clearly uses a significant amount debt to boost returns, as it has a debt to equity ratio of 2.60. I think the ROE is impressive, but it would have been assisted by the use of debt. Investors should think carefully about how a company might perform if it was unable to borrow so easily, because credit markets do change over time.
The Bottom Line On ROE
Return on equity is one way we can compare the business quality of different companies. Companies that can achieve high returns on equity without too much debt are generally of good quality. If two companies have around the same level of debt to equity, and one has a higher ROE, I’d generally prefer the one with higher ROE.
But when a business is high quality, the market often bids it up to a price that reflects this. It is important to consider other factors, such as future profit growth — and how much investment is required going forward. So I think it may be worth checking this free report on analyst forecasts for the company.
If you would prefer check out another company — one with potentially superior financials — then do not miss this free list of interesting companies, that have HIGH return on equity and low debt.
To help readers see past the short term volatility of the financial market, we aim to bring you a long-term focused research analysis purely driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis does not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements.
The author is an independent contributor and at the time of publication had no position in the stocks mentioned. For errors that warrant correction please contact the editor at editorial-team@simplywallst.com.