Today, the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University announced that its eRapid technology has been licensed to The iQ Group Global for COVID-19 diagnostic applications.
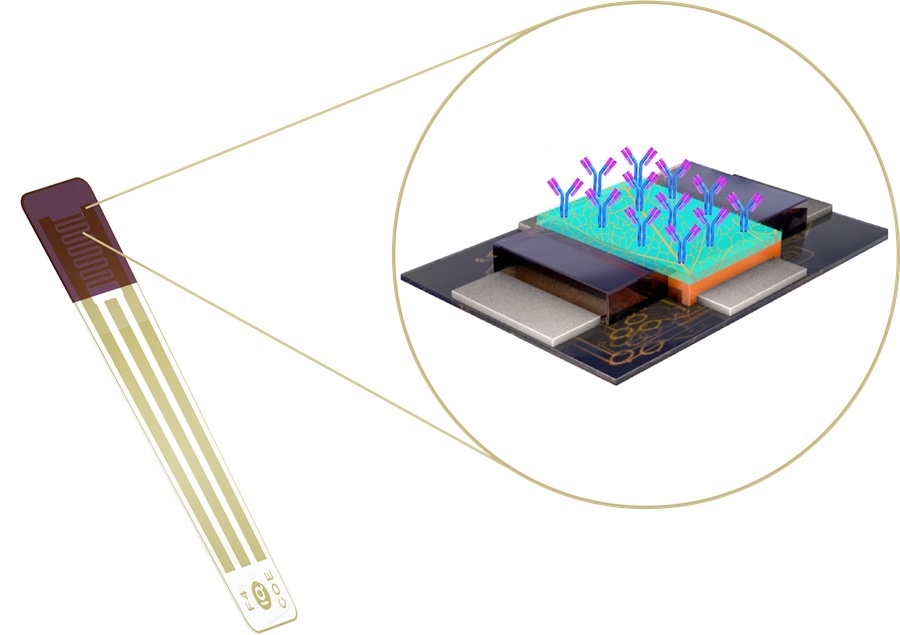
The Australian consortium will integrate the biomarker detection technology with its transistor technology to enable specific and sensitive SARS-CoV-2 testing in addressing the global diagnostic gap in the rampant coronavirus pandemic.
The licensing agreement was coordinated by Harvard's Office of Technology Development (OTD) in accordance with the University's commitment to the COVID-19 Technology Access Framework.
Developed in a cross-disciplinary team effort led by the Wyss' Founding Director Donald Ingber, M.D., Ph.D., and Wyss Senior Staff Scientist Pawan Jolly, Ph.D., the eRapid technology is a low-cost, affinity-based electrochemical sensing platform that can multiplex simultaneous detection and quantification of a broad range of biomarkers, including proteins, antibodies, RNA, and small molecules with high sensitivity and selectivity in small quantities of complex biological fluids, such as blood or saliva. Simultaneously analyzing the presence of multiple different biomarkers related to the patient's infection state can provide enhanced diagnostic sensitivity and specificity, and better inform physicians.
As part of the Institute's collective response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the team leveraged their eRapid technology to build an effective SARS-CoV-2 detection system to meet the long term challenge of providing point-of-care diagnostics for use in physician's offices, pharmacies, or at home, which might be used to identify whether a patient is actively infected or if he or she has been infected or vaccinated in the past and has developed an active immune response.
Broad, fast, and accurate COVID-19 diagnosis outside the hospital setting remains one of the main challenges in this relentless pandemic, especially now that we are clearly facing yet another wave of infections. Our eRapid technology offers the possibility of developing inexpensive diagnostic tests that have the potential to accurately determine the presence of infection, the stage of the infection, and the patient's response to the virus all simultaneously."
Donald Ingber, Judah Folkman Professor of Vascular Biology at Harvard Medical School and Boston Children's Hospital, and Professor of Bioengineering at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences
The eRapid technology is based on a novel, antifouling nanocomposite coating to which SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies are attached that capture viral proteins or RNA, or antibodies produced by infected individuals in response to the virus. Upon chemically detecting any one of these virus-specific molecules, the eRapid platform generates an electrical signal, and the strength of that signal correlates directly with the levels of target molecules present in the sample.
The antifouling coating enables eRapid technology to provide low cost electrochemical sensors with higher sensitivity and specificity, while the multiplexed nature of the devices allows them to validate diagnosis by quantifying the levels of multiple different viral components and host response molecules. As the coating also allows these devices to be re-used multiple times with consistent specificity and sensitivity, the costs of diagnostic assays can be reduced even further.
"eRapid's features and capabilities would make it an effective tool for easily tracing active immunity in infected individuals and those that recovered from COVID-19 to help determine their basis for resistance. Such a versatile platform that helps us better understand how the disease develops, persists, and can be controlled could be an invaluable asset in the fight against the pandemic," said Jolly, who helped lead this effort as part of the Wyss' Bioinspired Therapeutics & Diagnostics Platform, where the eRapid technology was developed and de-risked in a high-priority Institute Project with industry-minded expertise in technology and business development.
The iQ Group Global will integrate the Wyss' eRapid technology with its biosensor platform. A key component of the platform is the company's proprietary Organic Thin Film Transistor technology, which is able to significantly enhance electrical signals such as the ones generated by eRapid, and allow them to be read out in a smart device to provide diagnostic answers in real time.
Non-invasive, low cost and scalable SARS-Cov-2 antibody testing is urgently needed to estimate the incidence and prevalence of SARS-Cov-2 infection at the general population level. We intend to focus on placing this SARS-Cov 2-test as a potential companion diagnostic to the vaccination programs globally. Given the analytical characteristics of the biosensor and its stage of development, the combined technologies position us excellently to develop a more accurate, sensitive and real-time SARS-CoV-2 test for diagnostic, point-of-care testing, and pre-vaccination screening to meet this urgent global need."
Dr. George Syrmalis, Group CEO, The iQ Group Global