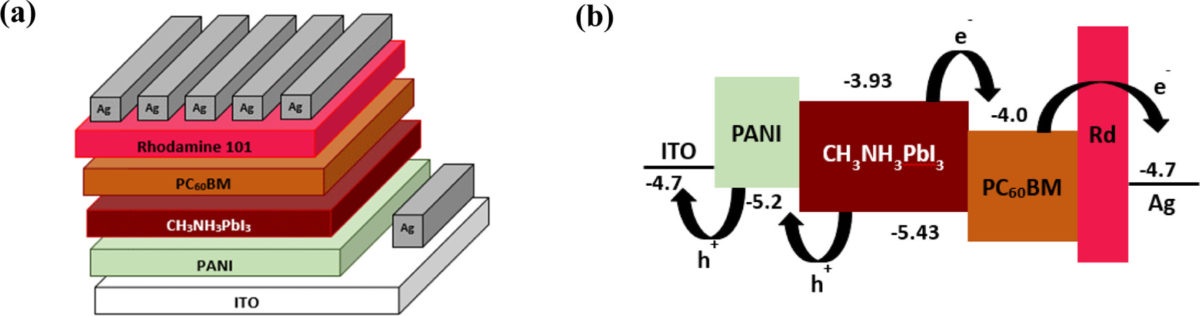
A US-Chinese research group has fabricated an inverted perovskite solar cell with a hole-transporting material (HTM) based on conducting polyaniline (PANI) polymer, instead of the commonly used PEDOT:PSS.
The scientists said the new polymer responds to the need to develop HTMs that provide superior properties, at a lower cost than PEDOT:PSS. Due to its electrical conductivity and mechanical properties, PANI is currently used in various applications, including drug delivery, photovoltaic cells, plastic batteries, display devices, microelectronics, and chemically modified electrodes, among others.
“Polyaniline is one such candidate as it exhibits attractive attributes such as high conductivity, environmental stability, low cost, easy synthesis, high purity, thin film transparency, and a high degree of processability which are suitable for perovskite solar cells,” the researchers said.
The electrochemically synthesized p-type doped PANI-based HTL showed high electrical conductivity after being doped with nitric acid (HNO3).
“The electrochemical polymerization method by cyclic voltammetry is the preferred method to prepare PANI,” the academics said. “The prepared polymer from this method can possess high purity and good adhesion with the hydrophilic substrate compared to the chemically prepared PANI, which is prone to impurities and poor adhesion to the substrate.”
Popular content
The PANI-based solar cell achieved an efficiency of up to 16.94%, which compares to 15.11% in a reference cell built with an HTL based on PEDOT:PSS. The researchers attributed the efficiency gain to the improved open-circuit voltage and short-circuit current.
The research group includes scientists from Syracuse University , South Dakota State University, and Huzhou University. The researchers introduced the cell technology in “Electrochemically Prepared Polyaniline as an Alternative to Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly(styrenesulfonate) for Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells,” which was recently published in ACS Publications.
“These results suggest that the PANI prepared using this easy, fast, and low-cost method can be an excellent alternative to the rather expensive PEDOT:PSS to further improve the PV performance and simultaneously reduce the cost of the perovskite PV technology,” they said.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.


By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.