Fear impacts quality of life for young adults with type 1 diabetes
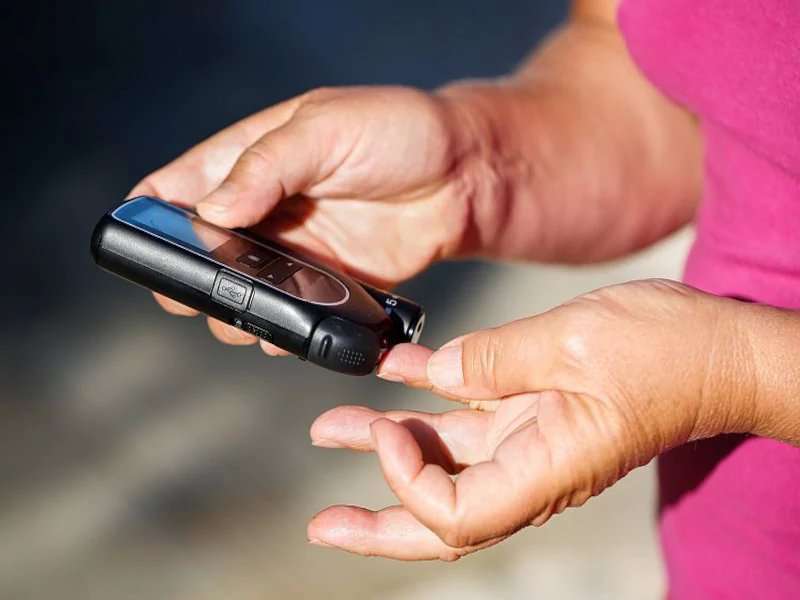

(HealthDay)—Fear of complications and frustration at the amount of time required to manage type 1 diabetes impact the quality of life of young adults with the disease, according to a study published in the December issue of The Diabetes Educator.
Denise A. Kent, Ph.D., R.N., and Laurie Quinn, Ph.D., R.N., both from the University of Illinois at Chicago, examined factors known to be associated with quality of life, including fear of complications, self-efficacy for diabetes self-management, and self-management of diabetes, among 180 young adults (aged 18 to 35 years) with type 1 diabetes.
The researchers found that quality of life was significantly associated with fear of hypoglycemia, fear of complications, and self-efficacy. Six in 10 report being afraid of long-term complications, 70 percent report being scared diabetes will affect their feet, and 42 percent worry very often about having a low-blood glucose crisis when asleep. However, quality of life was not associated with either diabetes self-management behaviors or diabetes knowledge. Fears extended beyond disease management and included fears of being denied insurance, the burden the disease places on their family, and even concerns about having children and getting a job.
"Young adults are engaging in developmental tasks and new relationships," Quinn said in a statement. "Minimizing their worries about diabetes will help them focus on the important new roles they are taking on personally and societally. It may also help people with diabetes have and maintain better quality of life in later stages of life."
More information: Abstract/Full Text
Copyright © 2018 HealthDay. All rights reserved.