This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
How the flu virus hacks our cells
Influenza epidemics, caused by influenza A or B viruses, result in acute respiratory infection. They kill half a million people worldwide every year. These viruses can also wreak havoc on animals, as in the case of avian flu. A team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) has identified how the influenza A virus manages to penetrate cells to infect them.
By attaching itself to a receptor on the cell surface, it hijacks the iron transport mechanism to start its infection cycle. By blocking the receptor involved, the researchers were also able to significantly reduce its ability to invade cells. These results, published in the journal PNAS, highlight a vulnerability that could be exploited to combat the virus.
Influenza viruses represent a major risk to human and animal health. Their potential for mutation makes them particularly elusive. "We already knew that the influenza A virus binds to sugar structures on the cell surface, then rolls along the cell surface until it finds a suitable entry point into the host cell. However, we did not know which proteins on the host cell surface marked this entry point, and how they favored the entry of the virus," explains Mirco Schmolke, Associate Professor in the Department of Microbiology and Molecular Medicine and in the Geneva Center for Inflammation Research (GCIR) at the UNIGE Faculty of Medicine, who led this work.
A receptor as a key to infection
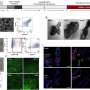
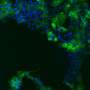
The scientists first identified cell surface proteins present in the vicinity of the viral hemagglutinin, the protein used by the influenza A virus to enter the cell. One of these proteins stood out: transferrin receptor 1. This acts as a revolving door transporting iron molecules into the cell, which are essential for many physiological functions.
"The influenza virus takes advantage of the continuous recycling of the transferrin receptor 1 to enter the cell and infect it," explains Béryl Mazel-Sanchez, a former post-doctoral researcher in Mirco Schmolke's laboratory and first author of this work.
"To confirm our discovery, we genetically engineered human lung cells to remove the transferrin receptor 1, or on the contrary to overexpress it. By deleting it in cells normally susceptible to infection, we prevented influenza A from entering. Conversely, by overexpressing it in cells normally resistant to infection, we made them easier to infect."
Inhibiting this mechanism
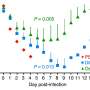
The research team then succeeded in reproducing this mechanism by inhibiting the transferrin receptor 1 using a chemical molecule. "We tested it successfully on human lung cells, on human lung tissue samples and on mice with several viral strains," says Béryl Mazel-Sanchez.
"In the presence of this inhibitor, the virus replicated much less. However, in view of its potentially oncogenic characteristics, this product cannot be used to treat humans." On the other hand, anti-cancer therapies based on the inhibition of the transferrin receptor are under development and could also be interesting in this context.
"Our discovery was made possible thanks to the excellent collaboration within the Faculty of Medicine as well as with the University Hospitals of Geneva (HUG) and the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics (SIB)," the authors add.
In addition to the transferrin receptor 1, scientists have identified some 30 other proteins whose role in the influenza A entry process remains to be deciphered. It is indeed likely that the virus uses a combination involving other receptors. "Although we are still far from a clinical application, blocking the transferrin receptor 1 could become a promising strategy for treating influenza virus infections in humans and potentially in animals."
More information: Beryl Mazel-Sanchez et al, Influenza A virus exploits transferrin receptor recycling to enter host cells, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2023). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2214936120
Journal information: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Provided by University of Geneva