Researchers experiment with tools to 'maneuver' medicine-carrying red blood cells
Scientists from the Moscow-based National Research Nuclear University MEPhI and the University of Oulu in Finland have completed a comprehensive joint study on the interaction of red blood cells for drug delivery using recent advances in medical nanotechnology. The research is expected to have major implications for the targeted delivery of drugs, an idea in nanomedicine aimed at concentrating medication in parts of the body affected by illness, while avoiding interactions with healthy tissue, and thus reducing both dosages and potentially dangerous side effects.
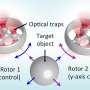
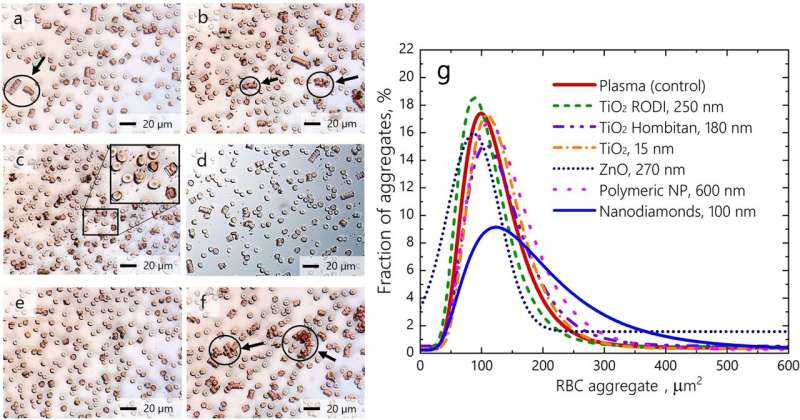
"We used optical laser-based tweezers, as well as phased and electron microscopy," said Dr. Igor Meglinski, co-author of the study. "Optical tweezers allowed us to create conditions for the interactions of blood cells that aren't possible to observe in ordinary circumstances. The combination of methods gives us the possibility of measuring the impact of various nanoparticles in the interaction of blood cells."
Optical tweezers are a relatively new scientific instrument designed to physically hold and move microscopic particles. Inventor Arthur Ashkin won the Nobel Prize for his creation in 2018.
The research by Russian and Finnish scientists, published in a recent issue of Scientific Reports, used this and other tools to study interactions between red blood cells for the purpose of further using them as a natural means to transport medicines. The idea is that blood cells can be loaded up with drugs, taking them to the precise location affected by disease, and thus reducing the risk of potential side effects associated with the non-directed application of medications.
If proven possible, the idea would have major implications, with researchers believing it would essentially become a "new paradigm" for nanomedicine and medicine in general. Until now, however, scientists have lacked the necessary research on the impact the nanoparticles combining to create various medicines have on red blood cells' behavior, and, more broadly, how that may impact a person's health.
In addition to plans to improve the technologies involved, researchers now plan to continue their work by expanding the range of tasks they can perform—including a study of the properties of red blood cells in the presence of various allergens and nanomaterials (not only drugs, but various toxic substances and poisons), as well as an analysis of their behavior when exposed to electromagnetic radiation, various diseases, and pathologies. The work is also expected be useful for immunotherapeutic tasks, and the creation of artificial blood.
More information: Tatiana Avsievich et al. Mutual interaction of red blood cells influenced by nanoparticles, Scientific Reports (2019). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-41643-x
Journal information: Scientific Reports
Provided by National Research Nuclear University