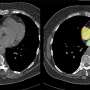
Nanomaterials
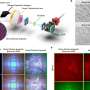
Research combines DNA origami and photolithography to move one step closer to molecular computers
Molecular computer components could represent a new IT revolution and help us create cheaper, faster, smaller, and more powerful computers. Yet researchers struggle to find ways to assemble them more reliably and efficiently.
13 minutes ago
0
0
Archaeology
Social change may explain decline in genetic diversity of the Y chromosome at the end of the Neolithic period
The emergence in the Neolithic of patrilineal social systems, in which children are affiliated with their father's lineage, may explain a spectacular decline in the genetic diversity of the Y chromosome observed worldwide ...
38 minutes ago
0
0

Biomolecular condensates: Study reveals poor predictive power of established liquid-liquid phase separation assays
Cells buzz with millions of different biomolecules that diffuse chaotically through their substructures, yet they manage to ensure exquisite functional and spatial specificity.
Cells buzz with millions of different biomolecules that diffuse chaotically through their substructures, yet they manage to ensure exquisite functional ...
Cell & Microbiology
59 minutes ago
0
0
Giant virus discovered in wastewater treatment plant infects deadly parasite
The single-celled organism Naegleria fowleri ranks among the deadliest human parasites. Researchers around Matthias Horn and Patrick Arthofer from the Center for Microbiology and Environmental ...
The single-celled organism Naegleria fowleri ranks among the deadliest human parasites. Researchers around Matthias Horn and Patrick Arthofer from the ...
Cell & Microbiology
25 minutes ago
0
0

Airborne observations of Asian monsoon sees ozone-depleting substances lofting into the stratosphere
Powerful monsoon winds, strengthened by a warming climate, are lofting unexpectedly large quantities of ozone-depleting substances high into the atmosphere over East Asia, new research ...
Powerful monsoon winds, strengthened by a warming climate, are lofting unexpectedly large quantities of ozone-depleting substances high into the atmosphere ...
Earth Sciences
59 minutes ago
0
0
Crinkled coatings could prevent medical implants from failing
Medical implants could fail less often when coated with a microscopically crinkled, ceramic material designed by researchers at the University of Michigan. The coating is described in a paper published in ACS Applied Materials ...
Nanomaterials
59 minutes ago
0
0
Enhanced CRISPR method enables stable insertion of large genes into the DNA of higher plants
Scientists at the Leibniz Institute of Plant Biochemistry (IPB) have succeeded for the first time in stably and precisely inserting large gene segments into the DNA of higher plants very efficiently. To do this, they optimized ...
Plants & Animals
16 minutes ago
0
0
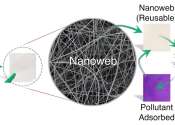
Nanofibers rid water of hazardous dyes: Researchers develop efficient filters based on cellulose waste
Using waste to purify water may sound counterintuitive. But at TU Wien, this is exactly what has now been achieved. Researchers have developed a special nanostructure to filter a widespread class of harmful dyes from water.
Nanomaterials
41 minutes ago
0
0

New method makes finding bat roosts easier for conservationists
A new algorithm is making it easier for ecologists and conservationists to find bat roost locations—reducing search areas by nearly 375 times their previous size. The technology combines microphone detector data with a ...
Ecology
11 minutes ago
0
0
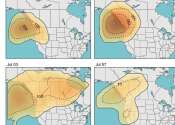
Climate change supercharged a heat dome, intensifying 2021 fire season, study finds
As a massive heat dome lingered over the Pacific Northwest three years ago, swaths of North America simmered—and then burned. Wildfires charred more than 18.5 million acres across the continent, with the most land burned ...
Earth Sciences
32 minutes ago
0
0
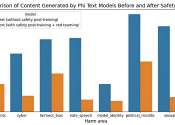
Microsoft claims that small, localized language models can be powerful as well
Microsoft has announced the development of a small, locally run family of AI language models called Phi-3 mini. In their Technical Report posted on the arXiv preprint server, the team behind the new SLM describes it as more ...
Securing competitiveness of energy-intensive industries through relocation: The pulling power of renewables
Countries with limited potential for renewables could save up to 20% of costs for green steel and up to 40% for green chemicals from green hydrogen if they relocated their energy-intensive production and would import from ...
Business
50 minutes ago
0
0

Immune cells on standby are constantly stimulated by healthy tissue, new study finds
When pathogens invade the body, the immune system must react immediately to prevent or contain an infection. But how do our defense cells stay ready when no attacker is in sight?
Genetics
32 minutes ago
0
0

The Future is Interdisciplinary
Find out how ACS can accelerate your research to keep up with the discoveries that are pushing us into science’s next frontier
 Medical Xpress
Medical Xpress

New study uses AI to predict malaria outbreaks in South Asia
Experimental strategy is the first to tackle fibrosis and scarring at the cellular level
Single-cell analysis reveals mechanisms of a common complication of Crohn's disease

Mini-colons advance colorectal cancer research
Discovering cancers of epigenetic origin without DNA mutation

Large study finds children with skin diseases suffer stigma, bullying and depression

Study uses wearable devices to examine 3- to 6-year-olds' impulsivity, inattentiveness

Longest study to date assesses cognitive impairment over time in adults with essential tremor

Exploring how the effects of racism impact sleep in adolescents

Survey finds loneliness epidemic runs deep among parents
 Tech Xplore
Tech Xplore

JFK Airport parking lot to become biggest solar array in New York

A simple 'twist' improves the engine of clean fuel generation

Emulating neurodegeneration and aging in artificial intelligence systems
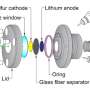
Storing and utilizing energy with innovative sulfur-based cathodes
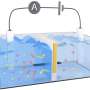
Salt battery harvests osmotic energy where the river meets the sea
Holographic displays offer a glimpse into an immersive future
Personalization has the potential to democratize who decides how LLMs behave

With a game show as his guide, researcher uses AI to predict deception
New model elevates UAV efficiency in next-gen wireless networks

Researchers achieve sustainable recovery of minerals from e-waste

New mitigation framework reduces bias in classification outcomes

New study uses AI to predict malaria outbreaks in South Asia
Researchers from NDORMS in collaboration with international institutions have demonstrated the potential of using environmental measurements and deep learning modeling to predict malaria outbreaks in South Asia. The study ...
Diseases, Conditions, Syndromes
48 minutes ago
0
0

AI designs active pharmaceutical ingredients quickly and easily based on protein structures
A new computer process developed by chemists at ETH Zurich makes it possible to generate active pharmaceutical ingredients quickly and easily based on a protein's three-dimensional surface. The new process, detailed in Nature ...
Biochemistry
48 minutes ago
1
0

New model extends theory of pattern formation to the nano-cosmos
A new model developed by scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Dynamics and Self-Organization (MPI-DS) extends the theory of elastic phase separation towards nanoscopic structures. Such patterns are frequent in biological ...
Nanophysics
48 minutes ago
0
0

Researchers create nanostructures for efficient and sustainable degradation of pollutants
The need for sustainable and environment-friendly solutions has accelerated the global demand for green and renewable technologies. In this regard, semiconductor photocatalysts have emerged as an attractive solution, owing ...
Nanomaterials
1 minute ago
0
0

Experimental strategy is the first to tackle fibrosis and scarring at the cellular level
Researchers at the Center for Genomic Regulation in Barcelona and the University of Cologne in Germany have developed a new experimental strategy to tackle scarring and fibrosis. Experiments with patient-derived human cells ...
Diseases, Conditions, Syndromes
52 minutes ago
0
0

Scientists at the MAJORANA Collaboration look for rule-violating electrons
In a new study published inNature Physics, scientists at the MAJORANA Collaboration have tested the stringency of charge conservation and Pauli's exclusion principles using underground detectors. Alessio Porcelli has published ...

Vast DNA tree of life for plants revealed by global science team using 1.8 billion letters of genetic code
A new paper published today (April 24) in the journal Nature by an international team of 279 scientists led by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew presents the most up-to-date understanding of the flowering plant tree of life.
Plants & Animals
1 hour ago
0
0

A chemical mystery solved—the reaction that explains large carbon sinks
A mystery that has puzzled the scientific community for more than 50 years has finally been solved. A team from Linköping University, Sweden, and Helmholtz Munich have discovered that a certain type of chemical reaction ...
Biochemistry
1 hour ago
0
1

Scientists develop novel liquid metal alloy system to synthesize diamond under moderate conditions
Did you know that 99% of synthetic diamonds are currently produced using high-pressure and high-temperature (HPHT) methods? A prevailing paradigm is that diamonds can only be grown using liquid metal catalysts in the "gigapascal ...
Analytical Chemistry
1 hour ago
0
1

New study reveals key role vision plays in sculpting brain development
Scientists have long known that our brains are organized into specialized areas, each responsible for distinct tasks. The visual cortex processes what we see, for instance, while the motor cortex governs movement. But how ...
Neuroscience
1 hour ago
0
0

Reintroduced gray wolf found dead in Larimer County, Colorado
One of 10 gray wolves reintroduced to Colorado in December was found dead in Larimer County, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service confirmed.

SpaceX launch marks 300th successful booster landing
SpaceX sent up the 30th launch from the Space Coast for the year on the evening of April 23, a mission that also featured the company's 300th successful booster recovery.

Steelhead trout, once thriving in Southern California, are declared endangered
Southern California's rivers and creeks once teemed with large, silvery fish that arrived from the ocean and swam upstream to spawn. But today, these fish are seldom seen.

Illinois residents encouraged to destroy the eggs of invasive insects to slow spread
While Chicagoans were alarmed to learn the spotted lanternfly had been found in Illinois last year, experts say spring is the time to take action against that insect—as well as another damaging invasive species that has ...

EU lawmakers agree to exit energy treaty over climate fears
The European Parliament on Wednesday backed the EU's withdrawal from an international energy treaty over concerns it offers too much protection to fossil fuel companies.

Extreme heat scorches Southeast Asia, bringing school closures and warnings
Extreme heat scorched parts of South and Southeast Asia Wednesday, prompting schools across the Philippines to suspend classes, heat warnings in the Thai capital and worshippers in Bangladesh to pray for rain.

Thousands in heatwave-hit Bangladesh pray for rain
Thousands of Bangladeshis gathered to pray for rain on Wednesday in the middle of an extreme heat wave that prompted authorities to shut down schools around the country.

Argentine students protest funding cuts to public universities
Tens of thousands of Argentine university students took to the streets Tuesday to protest cuts to higher public education, research and science under budget-slashing new President Javier Milei.

'So hot you can't breathe': Extreme heat hits the Philippines
Extreme heat scorched the Philippines on Wednesday, forcing thousands of schools to suspend in-person classes and prompting warnings for people to limit the amount of time spent outdoors.

Victims of China floods race to salvage property
Victims of severe floods in southern China raced on Wednesday to salvage property from the muddy waters as authorities warned of more heavy rains to come.

China to send three astronauts to Tiangong space station, part of its ambitious program
China's space agency is making final preparations to send a new crew to its space station on Thursday as part of its ambitious program that aims to put people on the moon by 2030.

Study: Sharing household chores can lead to income gains
Married women in patriarchal societies become more socially and financially independent when they participate in counseling with their spouses aimed at breaking gender norms, according to new research from a University of ...

Future hurricanes could compromise New England forests' ability to store and sequester carbon
Nature-based climate solutions can help mitigate climate change, especially in forested regions capable of storing and sequestering vast amounts of carbon. New research published in Global Change Biology indicates that a ...
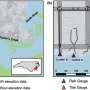
'Sunny day flooding' increases fecal contamination of coastal waters
A new study finds that "sunny day flooding," which occurs during high tides, increases the levels of fecal bacteria in coastal waters. While the elevated bacteria levels in the coastal waters tend to dissipate quickly, the ...

South Korean marginalized communities developed 'disaster subculture' living through extreme climate events, study finds
Locations around the globe are experiencing climate disasters on a regular basis. But some of the most marginalized populations experience disasters so often it has come to be normalized.

Study compares Salmonella rates in backyard, commercial poultry farm samples
In a comparison of differently sized poultry farms, researchers at North Carolina State University found that rates of Salmonella in fecal and environmental samples were more prevalent on larger commercial farms than on smaller ...
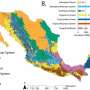
Researchers develop forest extent map for Mexico
To properly protect forests and evaluate the state of natural resources, conservation practices and environmental policies, it is important to have accurate information on an area's forest extent.

Investigating the efficacy of methods to stimulate adventitious rooting of Lindera benzoin stem cuttings
The variability among woody plants in their responses to asexual propagation techniques poses challenges and severe limits for commercial production. While some species readily root from stem cuttings, others are more difficult ...

Emotion can cause chickens to get red in the face
Studying emotion in animals is a complex research field, little explored up to now in birds, although reddening of the skin had already been observed in previous work on the blue-and-yellow macaw. An INRAE research team focused ...
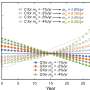
Warming climate is putting more metals into Colorado's mountain streams
Warming temperatures are causing a steady rise in copper, zinc, and sulfate in the waters of Colorado mountain streams affected by acid rock drainage. Concentrations of these metals have roughly doubled in these alpine streams ...