Development of Cd-free quantum dot synthesis technology
Prof. Jong-Soo Lee and his research team from the Department of Energy Science & Engineering, DGIST, developed a green-emitting Cd-Free quantum dot synthesis technology with high color reproduction rate. The newly developed quantum dot material is expected to be used in various photoelectric devices, including next-generation displays such as AR/VR.
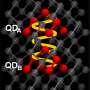
Quantum dots (QDs) are nano-sized semiconductor nanoparticles that are as small as ten-thousandth the size of a human hair. In particular, it has a high color reproduction performance and reproduces natural colors, making it suitable for its application in high dynamic range (HDR), which is used in ultra-high definition displays. Moreover, the material has higher color purity and photostability than other luminescent materials, emerging as the new material for various photoelectric devices, including next-generation displays.
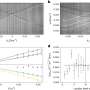
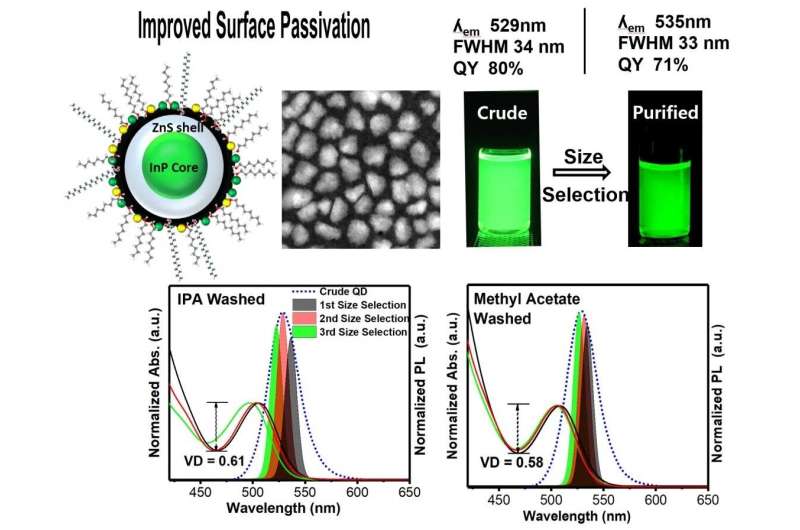
The color reproduction performance of QDs improves as the full width at half-maximum (FWHM) of the light-emitting wavelength of QD becomes smaller. Moreover, before the development of the proposed technology, the technical limit on the FWHM of photoluminescent (PL) peaks for the green-emitting Cd-Free QDs was 35nm.
Prof. Jong-Soo Lee and his team used a heat-up process to optimize the synthesis of InP-based QDs, and used zinc chloride (ZnCl2) and octanol(1-Octanol) for the stabilization of QD surface and succeeded in reducing the FWHM of QD PL peaks to less than 33nm.
In addition to achieving 80% quantum efficiency (QE), the research team also succeeded in securing the same level of stability as the existing QDs, which helped in solving the problem of quantum efficiency losses and reduction in stabilization.
Prof. Lee said, "The study proved that Cd-Free quantum dots can have FWHM of PL peaks smaller than 30nm, which was known as the technical limit before the introduction of proposed technology. Through follow-up studies, we hope to develop eco-friendly QDs with FWHM of PL peaks less than 30 nm as well as QE close to 100%, thus contributing to the next-generation displays and related industries."
Meanwhile, the research was supported by Mid-career Researchers Support Project funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea and by the research team of Hyper-connected Future Device Valleytronics, Pre-CoE Project, DGIST. The work was published in the Chemistry of Materials.
More information: Derrick Allan Taylor et al, Importance of Surface Functionalization and Purification for Narrow FWHM and Bright Green-Emitting InP Core–Multishell Quantum Dots via a Two-Step Growth Process, Chemistry of Materials (2021). DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.1c00348
Journal information: Chemistry of Materials
Provided by Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology