Scientists take important step toward using retinal cell transplants to treat blindness
Retinal cells derived from a cadaver human eye survived when transplanted into the eyes of primate models, an important advance in the development of cell therapy to treat blindness, according to a study published on January 14 in Stem Cell Reports.
The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), a layer of pigmented cells in the retina, functions as a barrier and regulator in the eye to maintain normal vision. RPE dysfunction can lead to eye disorders including macular degeneration and can cause blindness, which affects about 200 million people worldwide.
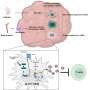
To restore this population of cells, the researchers extracted retinal stem cells from donated cadaver adult eyes, which can enable donor compatibility matching and can serve as a recurring source of human RPE. The team then assessed the safety and feasibility of implanting adult retinal stem cells into non-human primates.
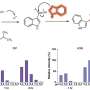
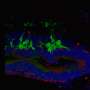
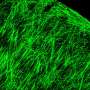
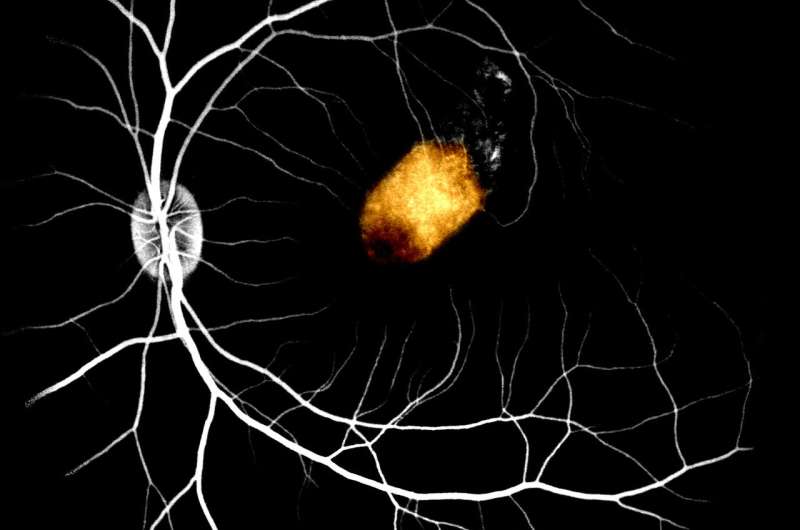
The study found that RPE patches transplanted under the macula, or the central part of the retina, remained stable and integrated in vivo for at least three months without serious side effects such as immune attack or light sensitivity. The researchers also found that the stem cell-derived RPE at least partially took over the function of the original RPE and was able to support the endogenous photoreceptor, which helps with light and water absorption among other functions.
"We have demonstrated human cadaver donor-derived RPE at least partially replaces function in the macula of a non-human primate," said Timothy Blenkinsop, Ph.D., co-lead investigator of the study and Assistant Professor of Cell, Developmental and Regenerative Biology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. "Human cadaver donor-derived cells can be safely transplanted underneath the retina and replace host function, and therefore may be a promising source for rescuing vision in patients with retina diseases. The results of this study suggest human adult donor RPE is safe to transplant, strengthening the argument for human clinical trials for treating retina disease."
The researchers said transplantation of RPE stem cells derived from human adult cadaver eyes to replace the defective RPE is a possible treatment for macular degeneration, but additional research on this approach is necessary. Future studies should explore whether RPE stem cells derived from cadaver adult eyes can restore vision in human patients and diseased non-human primate models.
More information: Stem Cell Reports (2021). dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2020.12.007