Improving the performance of electrodeless plasma thrusters for space propulsion

A Tohoku University researcher has increased the performance of a high-power electrodeless plasma thruster, moving us one step closer to deeper explorations into space.
Innovations in terrestrial transportation technologies, such as cars, trains, and aircraft, have driven historical technologies and industries so far; now, a similar breakthrough is occurring in space thanks to electric propulsion technology.
Electric propulsion is a technique utilizing electromagnetic fields to accelerate a propellant and to generate thrust that propels a spacecraft. Space agencies have pioneered electric propulsion technology as the future of space exploration.
Already, several space missions have successfully been completed using electric propulsion devices, such as gridded ion thrusters and Hall thrusters. Solar power is converted into thrust energy when the propellant becomes ionized, i.e., a plasma, and gets accelerated by electromagnetic fields. Yet, the electrodes necessary for these devices limit their lifetime, since they get exposed to and damaged by the plasma, especially at a high-power level.
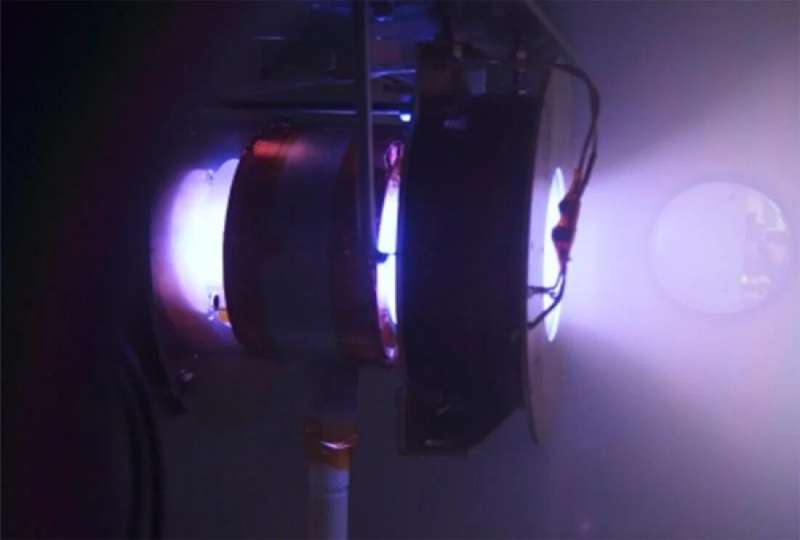
To circumvent this, scientists have turned to electrodeless plasma thrusters. One such technology harnesses radio frequency (rf) to generate plasma. An antenna emits radio waves into a cylindrical chamber to create plasma, where a magnetic nozzle channels and accelerates the plasma to generate thrust. MN rf plasma thrusters, or helicon thrusters as they are sometimes known, offer simplicity, operational flexibility, and a potentially high thrust-to-power ratio.
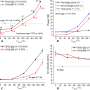
But the development of MN rf plasma thrusters has been stymied by the conversion efficiency of the rf power to thrust energy. Early experiments generated single digit conversion rates, but more recent studies have reached a modest outcome of 20%.
In a recent study published in Scientific Reports, Professor Kazunori Takahashi, from Tohoku University's Department of Electrical Engineering, has achieved a 30% conversion efficiency.
While mature electric propulsion devices often use xenon gas, which is expensive and difficult to supply in sufficient quantities, the current 30% efficiency was obtained with argon propellant. This indicates that a MN rf plasma thruster would reduce the cost and the resource load from the Earth.
"Applying a cusp-type magnetic field inhibited the energy loss that generally occurs to the plasma source wall," Takahashi said. "The breakthrough opens the door to advances in high-power space transportation technology."
More information: Kazunori Takahashi, Thirty percent conversion efficiency from radiofrequency power to thrust energy in a magnetic nozzle plasma thruster, Scientific Reports (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-22789-7
Journal information: Scientific Reports
Provided by Tohoku University