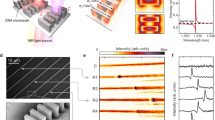
Abstract
Sequence-specific detection of polynucleotides typically requires modified reporter probes that are labeled with radioactive, fluorescent, or luminescent moieties. Although these detection methods are capable of high sensitivity, they require instrumentation for signal detection. In certain settings, such as clinical point of care, instrumentation might be impractical or unavailable. Here we describe a detection approach in which formation of a nucleic acid hybrid is enzymatically transduced into a molecular thin film that can be visually detected in white light. The system exploits a flat, optically coated silicon-based surface to which capture oligonucleotides are covalently attached. The optimized system is capable of detection of nucleic acid targets present at sub-attomole levels. To supplement visual detection, signals can be quantitated by a charge-coupled device. The design and composition of the optical surface, optimization of immobilization chemistry for attachment of capture probes, and characterization of the efficiency of the hybridization process are presented. We describe the application of this system to detection of a clinically relevant target, the mecA gene present in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kricka, L.J. Nucleic acid detection technologies–labels, strategies, and formats . Clin. Chem. 45, 453–458 (1999).
Whitcombe, D., Newton, C.R. & Little, S. Advances in approaches to DNA-based diagnostics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 9, 602–608 (1998).
Sandstrom, T., Stenberg, M. & Nygren, H. Visual detection of organic monomolecular films by interference colors. Appl. Optics 24, 472– 479 (1985).
Ostroff, R., Hopkins, D., Haeberli, A.B., Baouchi, W. & Polisky, B. Thin film biosensor for rapid visual detection of nucleic acid targets. Clin. Chem. 45, 1659–1664 (1999).
Urdea, M.S. et al. A comparison of non-radioisotopic hybridization assay methods using fluorescent, chemiluminescent and enzyme labeled synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 16, 4937– 4957 (1998).
The Committee on Colorimetry of the Optical Society of America. The science of color. (Edwards Brothers, Inc., Ann Arbor, MI; 1953).
Born, M. & Wolf, E. Principles of optics, Edn. 6. (Pergamon Press, Oxford, UK; 1980).
Running, J.A. & Urdea, M.S. A procedure for productive coupling of synthetic oligonucleotides to polystyrene microtiter wells for hybridization capture. BioTechniques 8, 276–277 (1990).
Brown, D.F.J. & Reynolds, P.E. Intrinsic resistance to β-lactam antibiotics in Staphylococcus aureus. FEBS Lett. 122, 275–278 (1980).
Hartman, B.J. & Tomasz, A. Low-affinity penicillin-binding protein associated with β-lactam resistance in Staphylococcus aureus . J. Bacteriol. 158, 513– 516 (1984).
Covalciuc, K.A., Webb, K.H. & Carlson, C.A. Comparison of four clinical specimen types for detection of Influenza A and B viruses by optical immunoassay (FLU OIA Test) and cell culture methods. J. Clin. Microbiol. 37, 3971–3974 (1999).
Gerber, M.A. et al. Optical immunoassay test for group A β-hemolytic streptococcal pharyngitis. JAMA 277, 899– 903 (1997).
Bobrow, M.N., Shaughnessy, K.J. & Litt, G.J. Catalyzed reporter deposition. II. Application to membrane immunoassays. J. Immunol. Methods 137, 103–112 (1991).
Lin, V.S.-Y., Motesharei, K., Dancil, K.-P.S., Sailor, M.J. & Ghadiri, M.R. A porous silicon-based optical interferometric biosenor. Science 278, 840–843 (1997).
Elghanian, R., Storhoff, J.J., Mucic, R.C., Letsinger, R.L. & Mirkin, C.A. Selective colorimetric detection of polynucleotides based on the distance-dependent optical properties of gold nanoparticles. Science 277, 1078 –1080 (1997).
Rule, G.S., Montagna, R.A. & Durst, R.A. Rapid method for visual identification of specific DNA sequences based on DNA-tagged liposomes. Clin. Chem. 42, 1206–1209 (1996).
Pospiech, A. & Neumann, B. A versatile quick-prep of genomic DNA from gram-positive bacteria. Trends Genet. 11, 217–218 (1995).
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Rachel Ostroff and Dr. Diana Maul for advice and critical evaluation of the manuscript. We also thank Wahab Baouchi for preparation of the optical surfaces, Chris High for preparation of the figures, and Brenda Bolton for assistance in preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jenison, R., Yang, S., Haeberli, A. et al. Interference-based detection of nucleic acid targets on optically coated silicon. Nat Biotechnol 19, 62–65 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/83530
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/83530
This article is cited by
-
Clinically feasible method for assessing leukocyte rheology in whole blood
Heart and Vessels (2020)
-
Helicase-dependent isothermal amplification: a novel tool in the development of molecular-based analytical systems for rapid pathogen detection
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (2018)
-
A simple and reliable qualitative detection of six foodstuff powders using optical thin-film biosensor chips
European Food Research and Technology (2013)
-
Direct optical detection in bioanalysis: an update
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (2010)
-
Rapid and reliable detection of 11 food-borne pathogens using thin-film biosensor chips
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2010)